Philosophy
Explore formal logic, epistemology, decision theory, ethics, and game theory through interactive simulations. Build natural deduction proofs, update beliefs with Bayes' rule, and compare moral frameworks on classic dilemmas. These tools bring analytical philosophy to life, from logical paradoxes to evolutionary game theory and social choice theory.
Formal Logic & Paradoxes
Construct natural deduction and sequent calculus proofs. Explore Russell's paradox, the liar sentence, and the Sorites paradox. See how formal systems handle vagueness and self-reference.
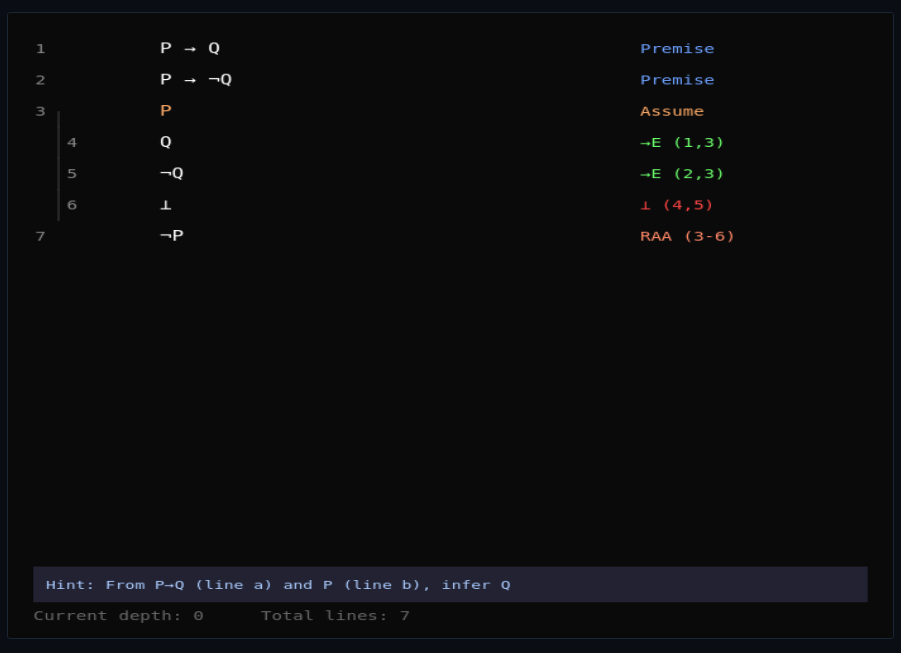
Natural Deduction Proof Builder
Build formal proofs step by step using introduction and elimination rules—prove theorems in propositional logic
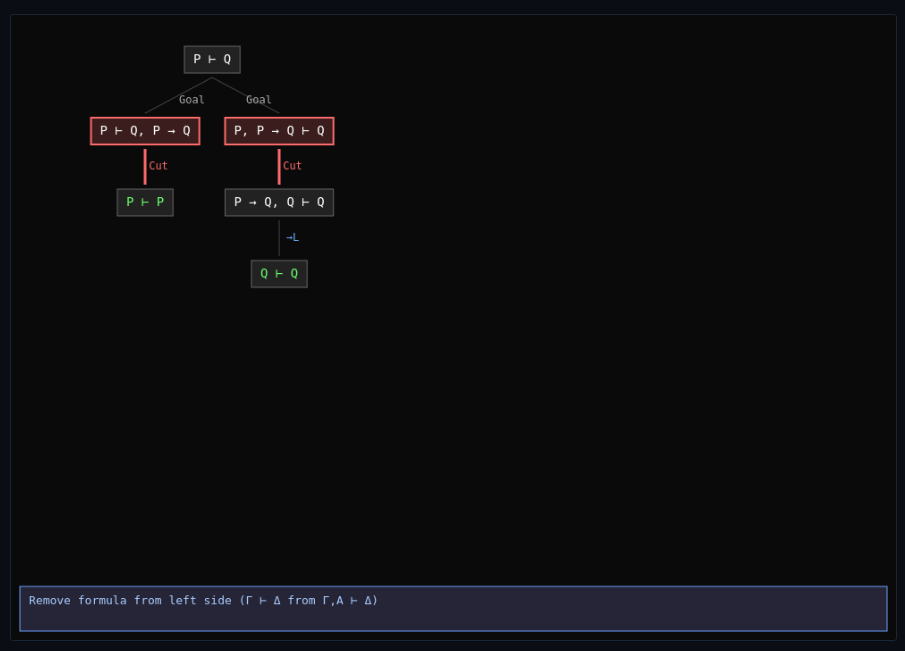
Sequent Calculus & Cut Elimination
Construct sequent calculus derivations—apply structural rules and cut elimination
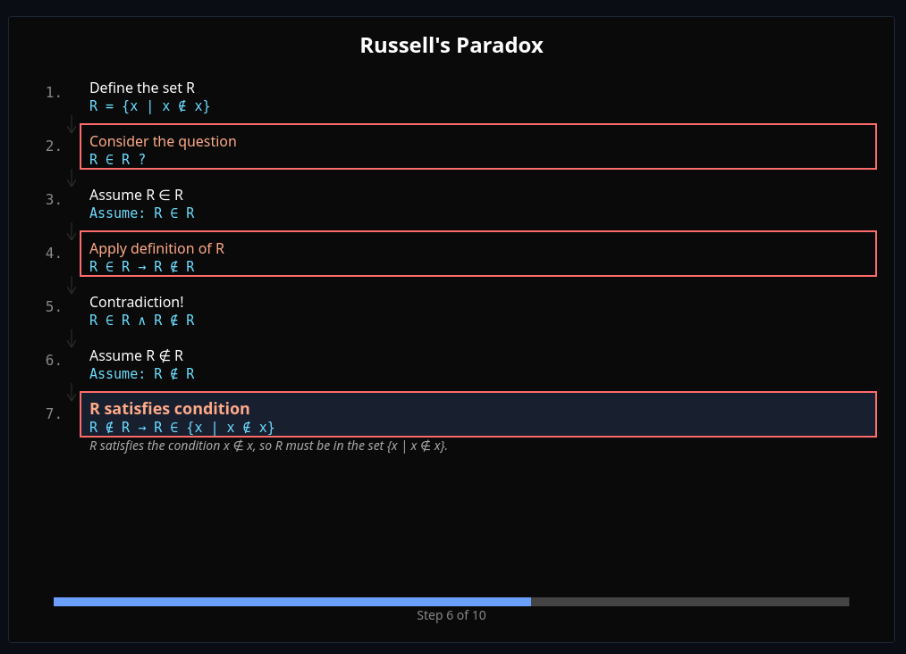
Logical Paradoxes Explorer
Explore Russell's paradox, the liar sentence, and Curry's paradox—see formal derivations and resolution strategies
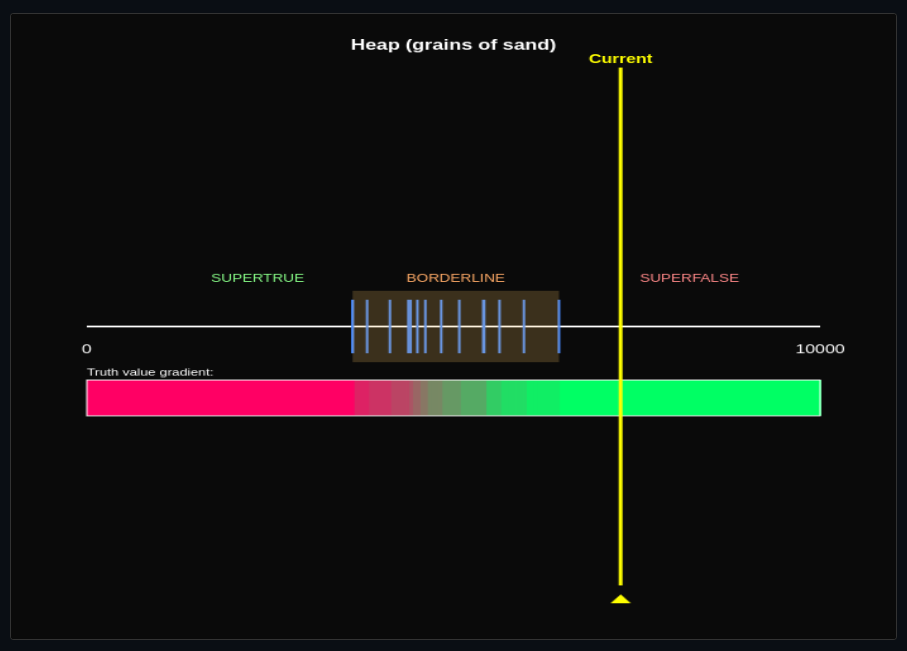
Sorites Paradox & Vagueness
Apply precisifications to vague predicates—explore supervaluationism and the Sorites paradox
Epistemology & Belief Revision
Update beliefs with Bayes' rule and Jeffrey conditioning. Explore coherence through Dutch book arguments, and navigate epistemic peer disagreement with equal-weight and steadfast views.
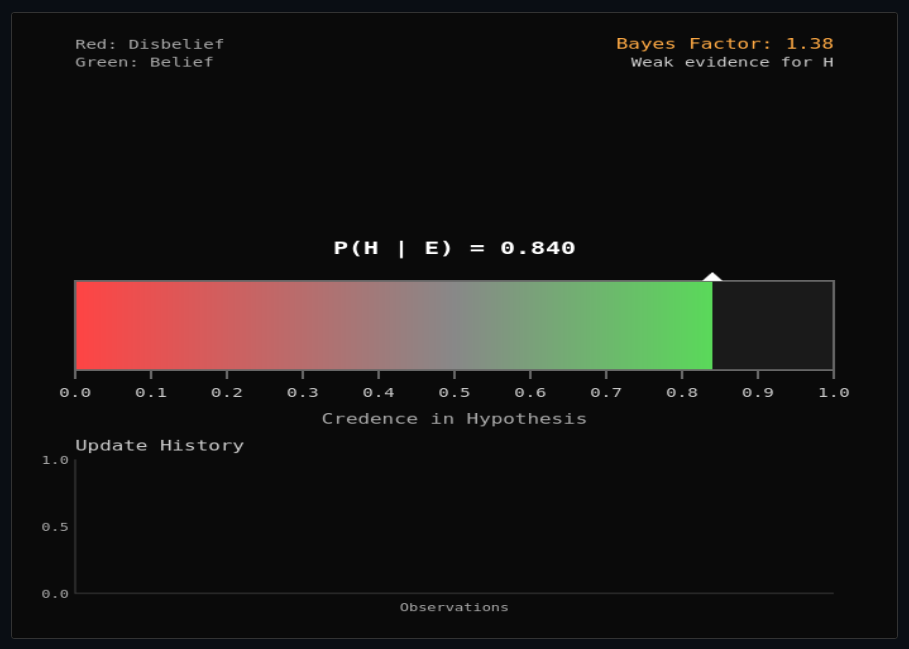
Bayesian Belief Updating
Update beliefs with Bayes' rule and Jeffrey conditioning—explore rational belief change
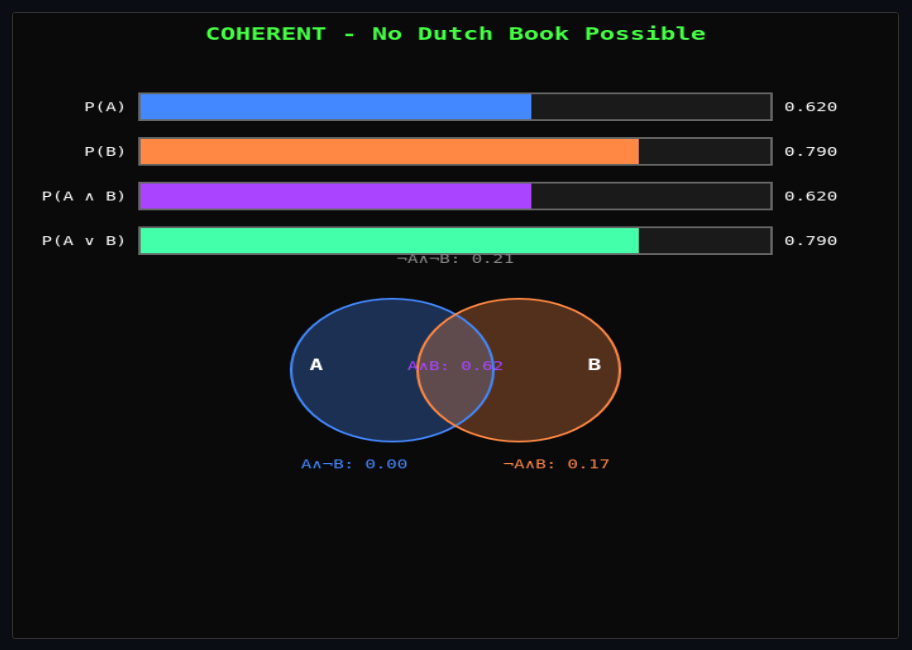
Dutch Book Arguments
Construct sure-loss betting scenarios against incoherent credences—see why probabilities must be coherent
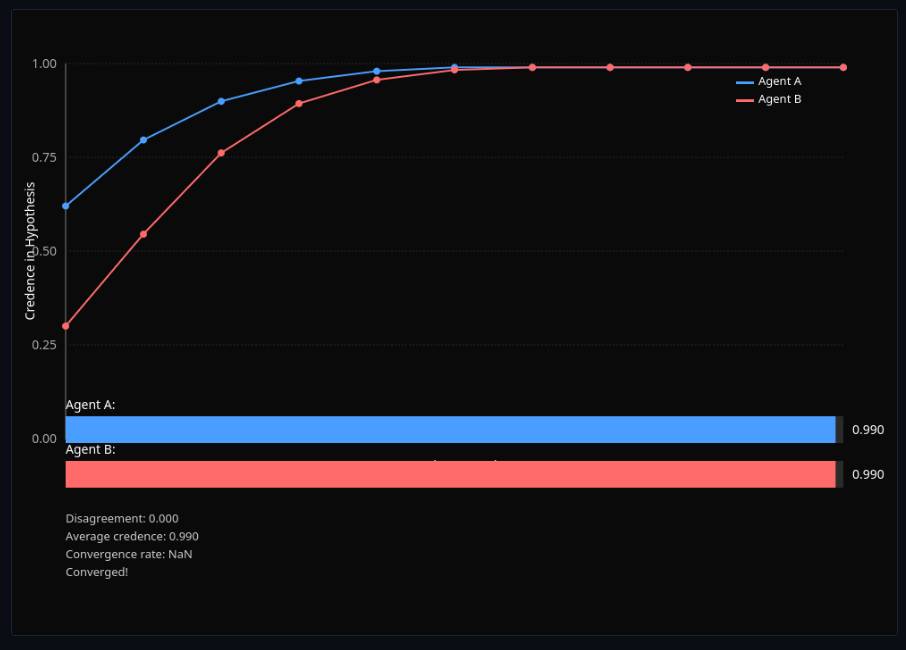
Epistemic Peer Disagreement
Update beliefs after learning an epistemic peer disagrees—compare equal-weight and steadfast approaches
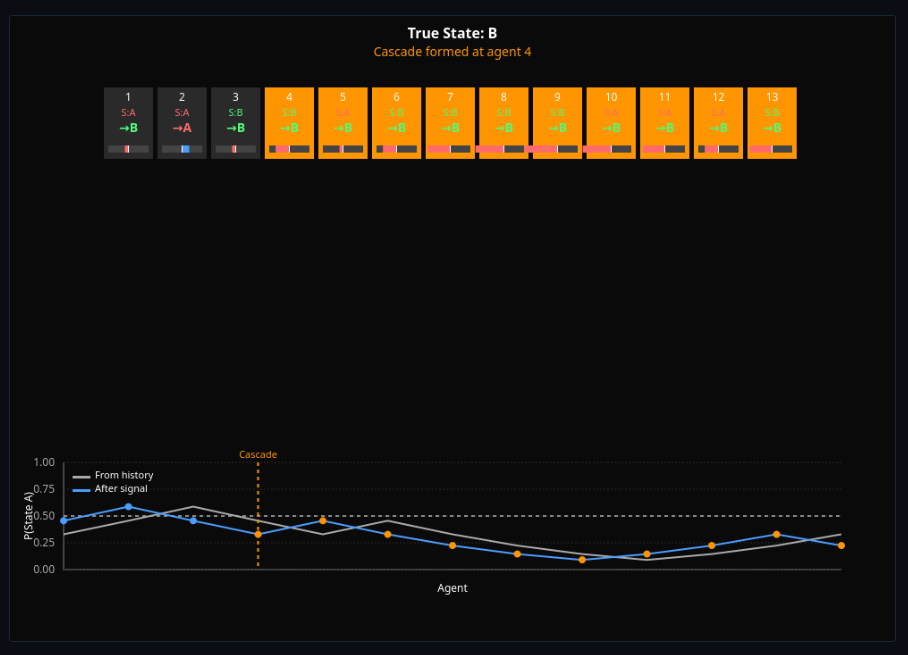
Information Cascades & Herding
Watch agents observe predecessors and sometimes ignore their own signals—see informational herding emerge
Causation & Decision Theory
Build causal graphs with Pearl's do-calculus and distinguish correlation from causation. Face Newcomb's paradox and compare evidential, causal, and functional decision theories. Model loss aversion with prospect theory.
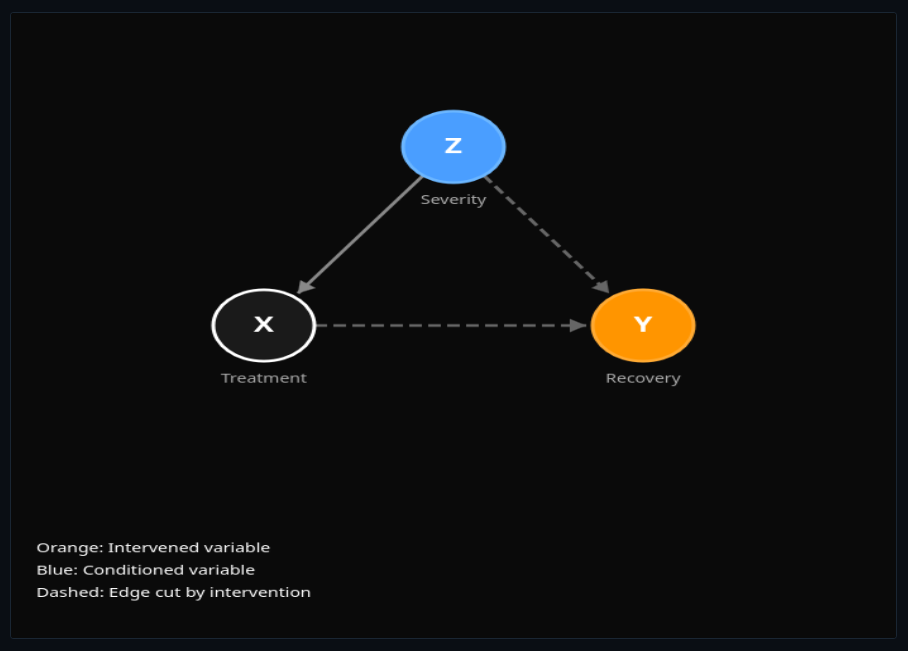
Pearl's Causal Calculus
Build causal graphs and apply Pearl's do-calculus—distinguish correlation from causation with interventions
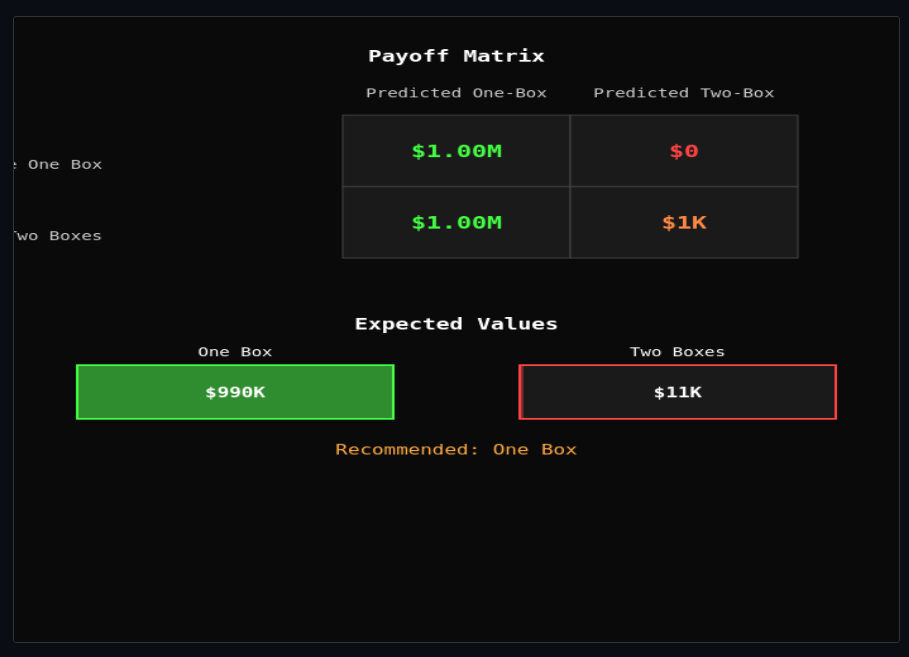
Newcomb's Paradox: Decision Theories
Choose one box or two in Newcomb's problem—compare evidential, causal, and functional decision theory recommendations
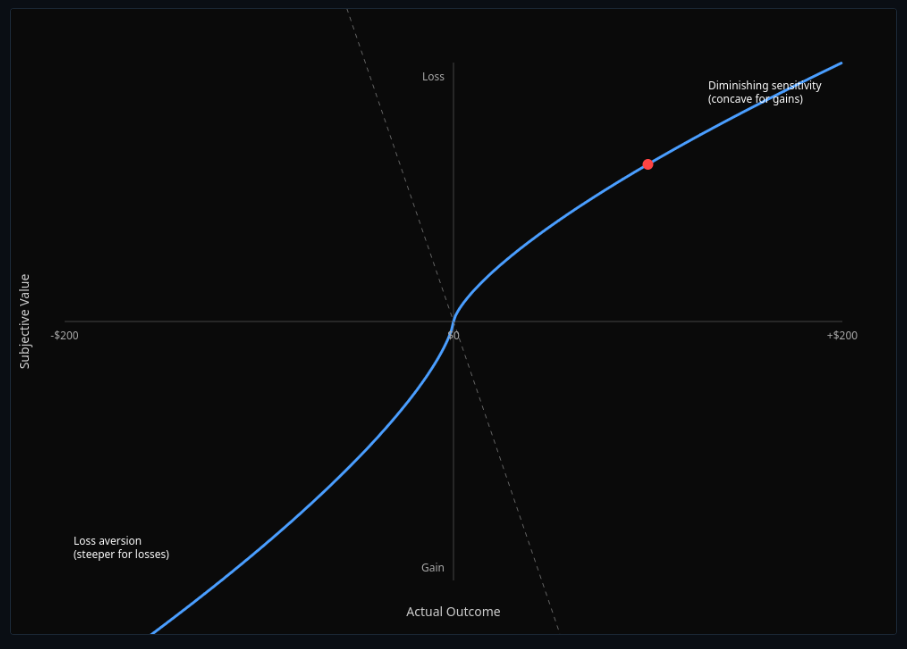
Prospect Theory & Loss Aversion
Adjust reference points and see loss aversion and probability weighting—model real decision-making biases
Game Theory & Cooperation
Run iterated prisoner's dilemma tournaments and watch cooperation evolve. Find Schelling points in coordination games and discover how signaling systems emerge through separating equilibria.

Iterated Prisoner's Dilemma Tournament
Run tournaments of strategies in iterated prisoner's dilemma—watch cooperation evolve through reciprocity
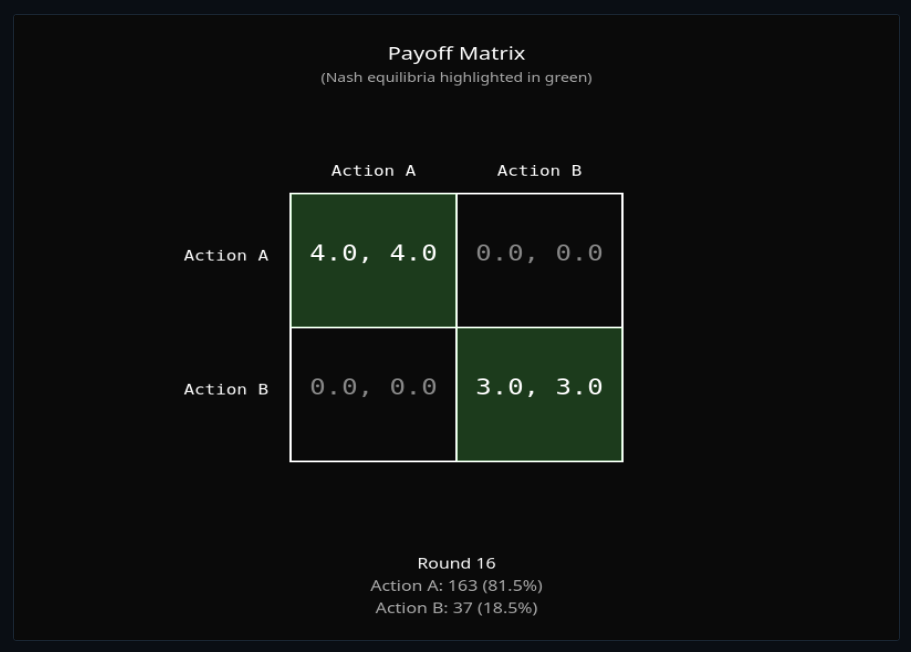
Coordination & Schelling Points
Find Schelling points in coordination games—explore focal equilibria and convention formation
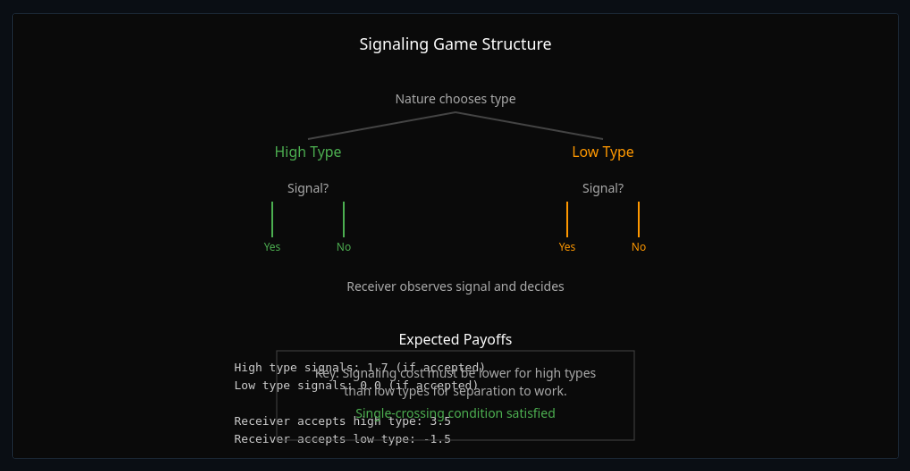
Signaling Equilibria
Evolve signaling systems and find pooling vs separating equilibria—see how communication emerges
Normative Ethics
Explore moral frameworks through classic dilemmas. Compare utilitarian, deontological, and contractualist reasoning. Aggregate utilities with different social welfare functions and act under moral uncertainty.
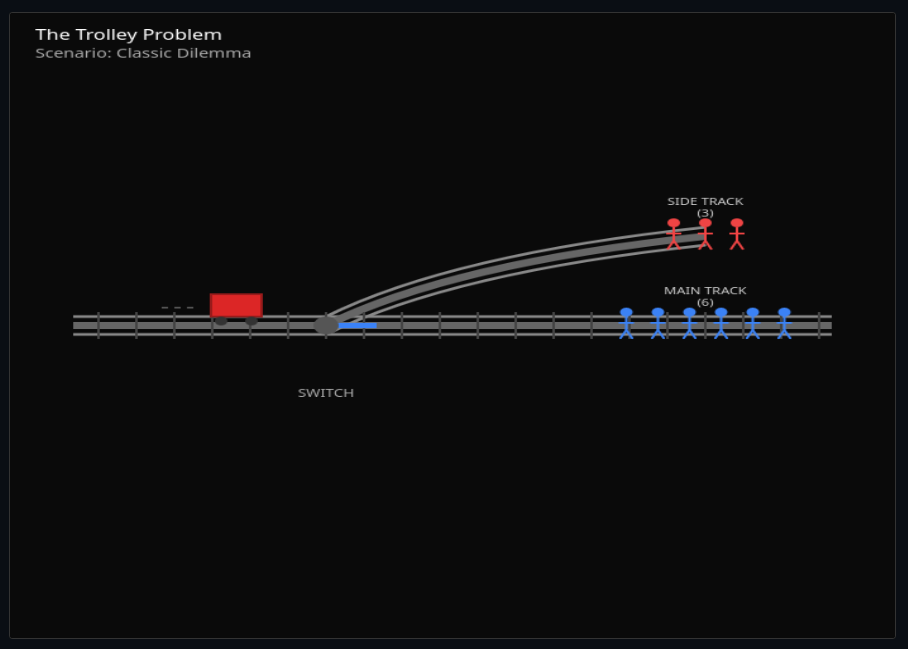
The Trolley Problem Variations
Pull the lever or push the man—compare utilitarian calculations with deontological constraints
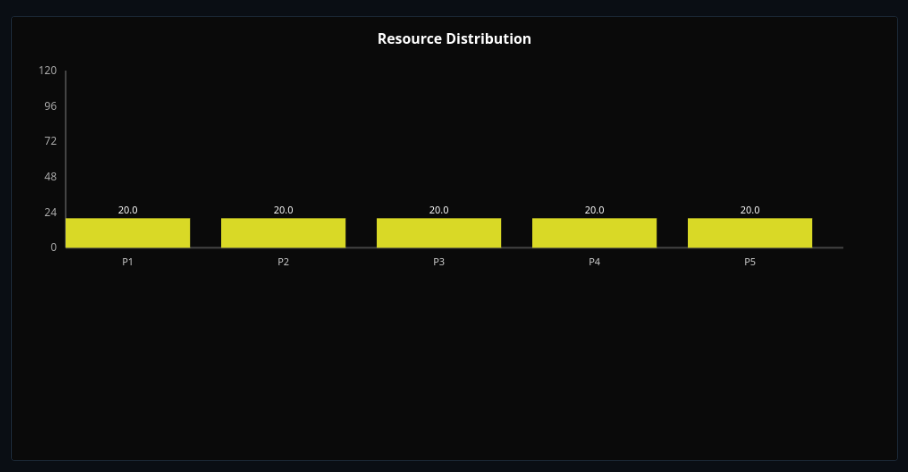
Social Welfare Aggregation
Aggregate individual utilities with utilitarian, prioritarian, and egalitarian social welfare functions—see how they treat inequality
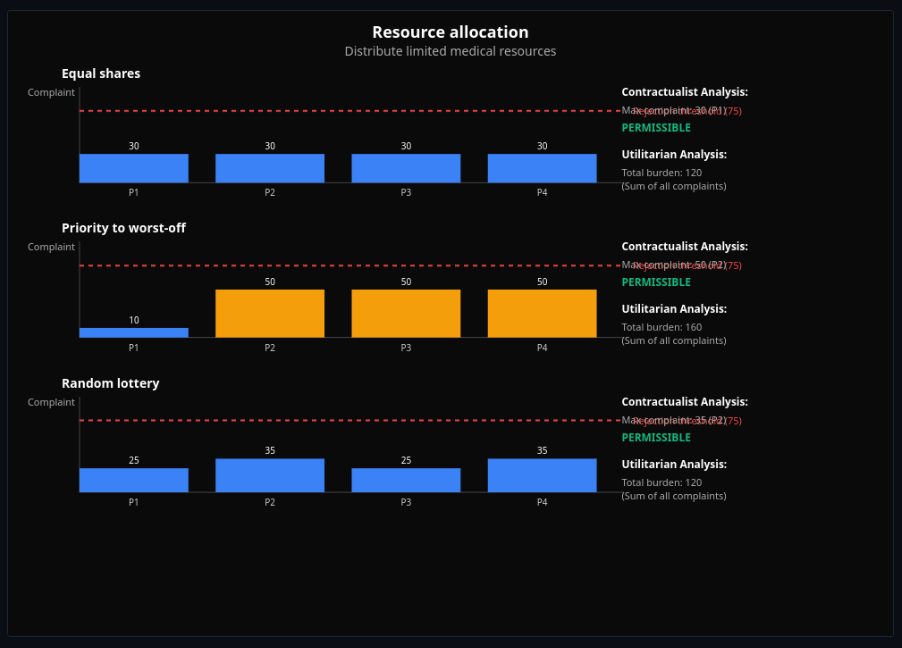
Contractualist Moral Reasoning
Evaluate principles by reasonable rejection—apply Scanlon's contractualist framework to moral dilemmas
Acting Under Moral Uncertainty
Choose actions under uncertainty about which moral theory is correct—explore choiceworthiness and moral hedging
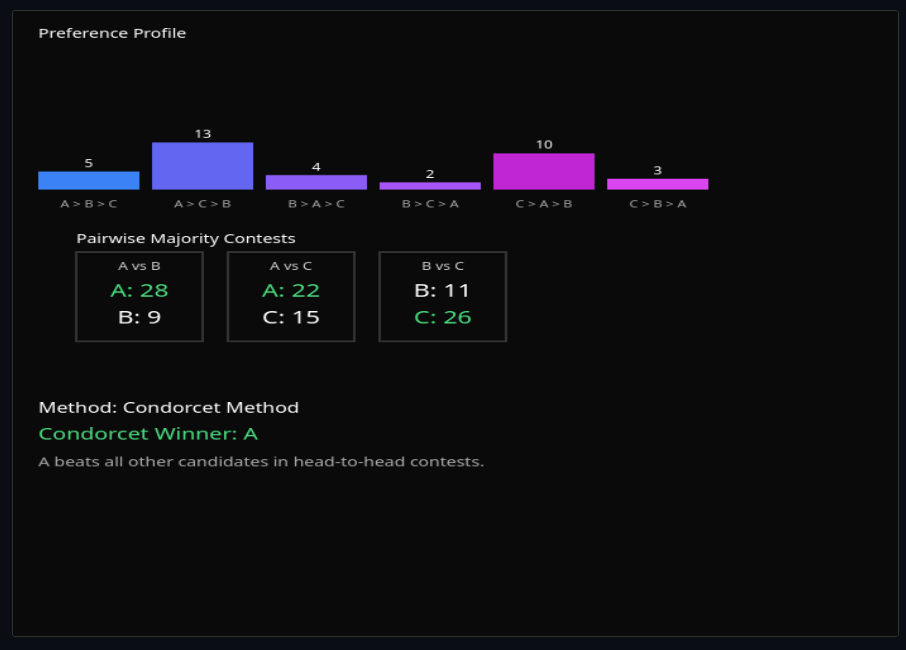
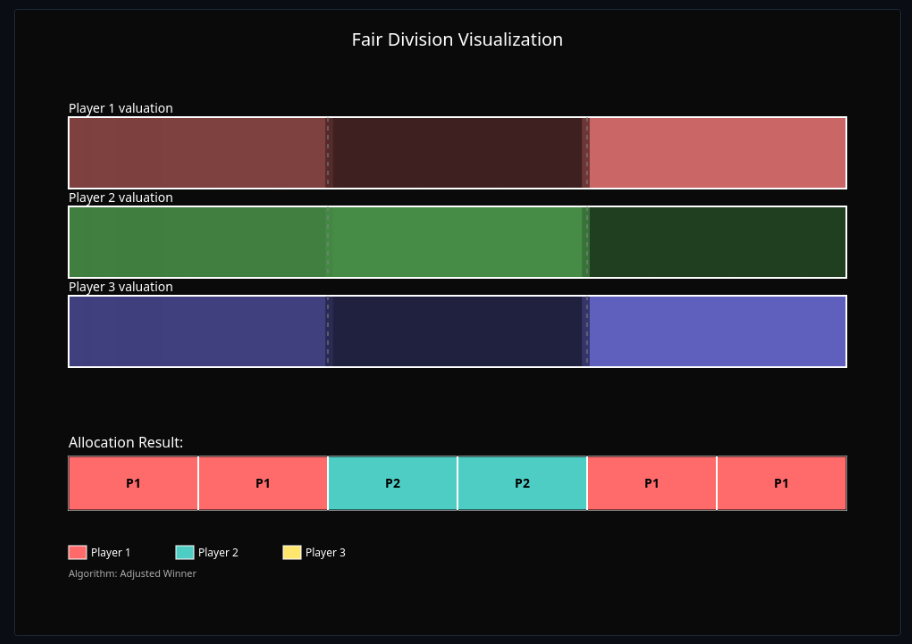
Social Choice Theory
Run elections with different voting systems and discover Arrow's impossibility theorem. Divide resources fairly with envy-free cake-cutting protocols.